Subtotal ₹0.00
Shopping cart
Subscribe to out newsletter today to receive latest news administrate cost effective for tactical data.
Boarding Para,Word No-2,Dinhata,Cooch Behar-736135
Call Us
+91 9734 088 336
Every Day (Open )
Subscribe to out newsletter today to receive latest news administrate cost effective for tactical data.
Boarding Para,Word No-2,Dinhata,Cooch Behar-736135
Call Us
Every Day (Open )
Monday - Tuesday :8 am - 11.30 pm
Wednesday - Thursday :8 am - 8 pm
Friday :8 am - 8 pm
Saturday :8 am - 8 pm
Sunday :8 am - 8 pm
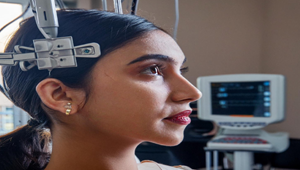
An ECG, or electrocardiogram, is a medical test that measures the electrical activity of the heart over a period of time. It is a non-invasive procedure commonly used to assess the heart’s rhythm and electrical conduction system. During an ECG, electrodes (small adhesive patches) are placed on the skin of the chest, arms, and legs. These electrodes detect the electrical signals generated by the heart as it beats and transmit them to a machine that records the signals as a series of waves or tracings on paper or digitally on a computer screen.
The electrical activity recorded by an ECG provides valuable information about various aspects of heart function, including:
1) Heart rate: The number of heartbeats per minute (bpm).
2) Rhythm: The regularity or irregularity of the heart’s electrical impulses.
3) Conduction abnormalities: Any disturbances in the electrical pathways of the heart, such as blockages or delays.
4) Heart muscle damage: Signs of heart attacks, ischemia (lack of blood flow to the heart muscle), or other cardiac conditions.
ECGs are commonly performed as part of routine medical examinations, during evaluations of symptoms such as chest pain or palpitations, before surgeries, or as part of cardiac monitoring in hospitalized patients. They are interpreted by healthcare professionals, such as cardiologists or primary care physicians, to aid in the diagnosis and management of various heart conditions.
| Sl.No | ECG |
|---|---|
| 1 | ECG |